Rasmussen Presidential Poll Overview
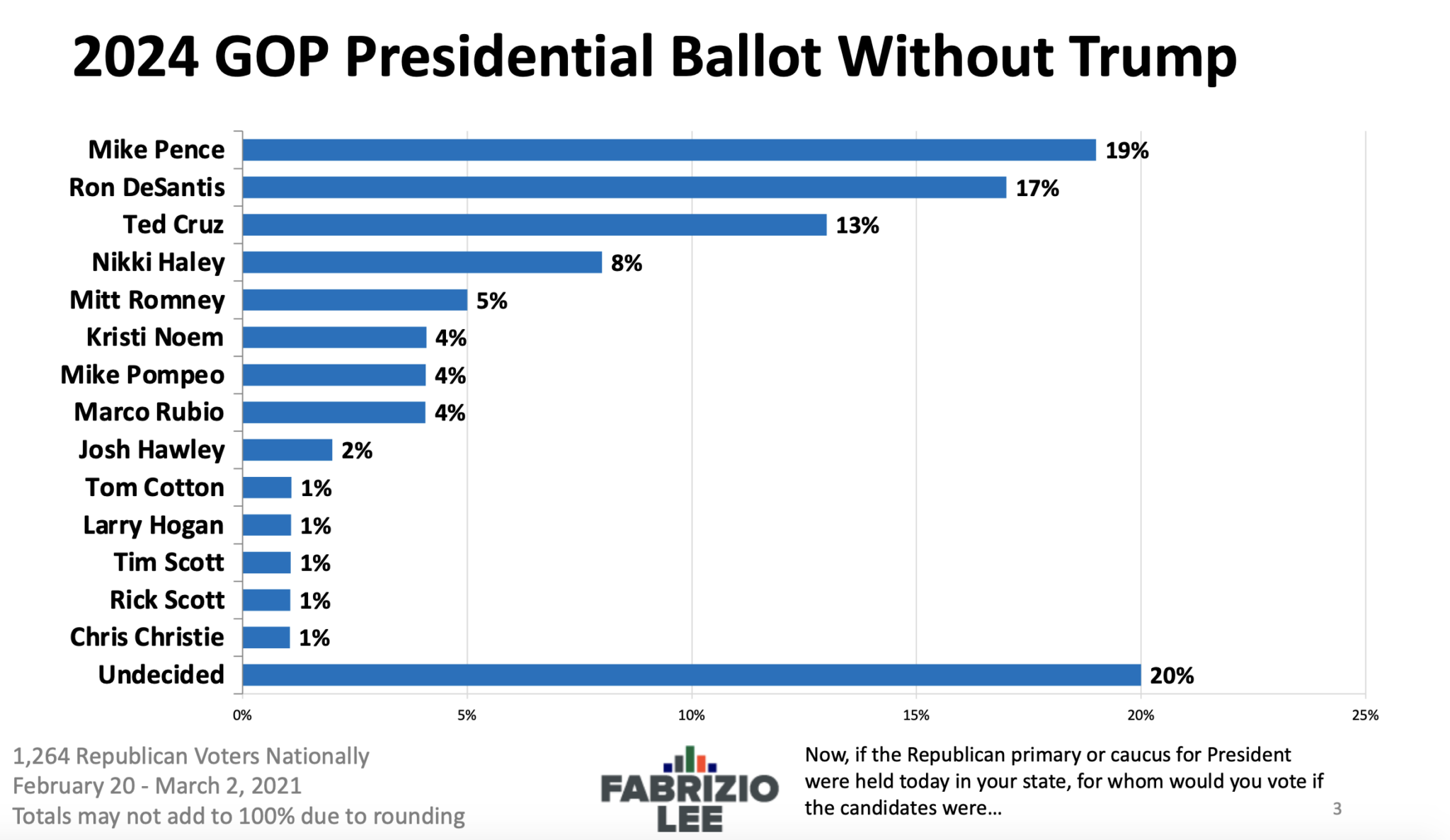
The Rasmussen Reports organization has been a prominent player in the field of political polling for over two decades, known for its unique methodology and real-time tracking of public opinion. This overview delves into the history of Rasmussen Reports, its polling methodology, and the types of questions asked in its presidential polls.
History of Rasmussen Reports
Rasmussen Reports was founded in 1999 by Scott Rasmussen, a political strategist and pollster. The organization quickly gained recognition for its focus on tracking public opinion on a daily basis, providing insights into the political landscape and electoral dynamics. Rasmussen Reports gained prominence during the 2000 presidential election, where its polling data proved to be accurate in predicting the close outcome of the race. Since then, Rasmussen Reports has become a widely respected source of political polling data, consistently providing insights into the views and preferences of the American public.
Methodology of Rasmussen Presidential Polls
Rasmussen Reports employs a multi-pronged approach to conducting its presidential polls, emphasizing a combination of traditional telephone surveys and online data collection methods.
Sample Size and Weighting
Rasmussen Reports typically conducts its presidential polls with a sample size of 1,000 likely voters. This sample size is considered statistically significant for providing reliable estimates of public opinion. The organization uses a complex weighting system to ensure that the sample reflects the demographic makeup of the American electorate. This weighting process takes into account factors such as age, gender, race, ethnicity, education level, and geographic location.
Data Collection Methods
Rasmussen Reports uses a combination of traditional telephone surveys and online data collection methods to gather its polling data. Telephone surveys are conducted through a random sampling process, ensuring that each household has an equal chance of being selected for participation. Online data collection methods involve surveying individuals who have opted to participate in online polling panels. This approach allows Rasmussen Reports to reach a broader audience and collect data from individuals who may not be reachable through traditional telephone surveys.
Types of Questions in Rasmussen Presidential Polls
Rasmussen presidential polls typically cover a wide range of topics, including:
Demographic Information
To understand the characteristics of the electorate, Rasmussen Reports collects demographic information from respondents, including age, gender, race, ethnicity, education level, and geographic location. This data is used to ensure that the sample reflects the demographic makeup of the American electorate and to analyze the relationship between demographic characteristics and voting preferences.
Voting Intentions
Rasmussen presidential polls focus on gauging voting intentions among likely voters. Respondents are asked about their preferred candidate in the upcoming presidential election, providing insights into the electoral landscape and the level of support for each candidate.
Policy Preferences
Rasmussen presidential polls also explore the policy preferences of likely voters. Respondents are asked about their views on a range of issues, such as the economy, healthcare, education, immigration, and foreign policy. This information provides insights into the priorities of the electorate and the issues that are most important to voters.
Analyzing Rasmussen Presidential Poll Results
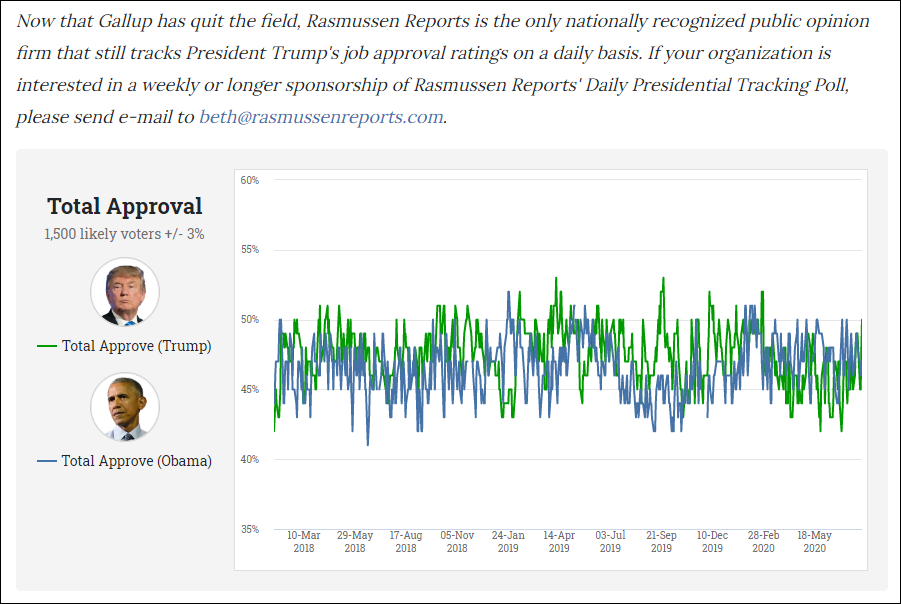
Rasmussen Reports is a well-known polling organization that conducts surveys on a wide range of topics, including presidential elections. Analyzing Rasmussen presidential poll results can provide valuable insights into voter sentiment, candidate performance, and the potential trajectory of the election.
Comparing Rasmussen Presidential Poll Results with Other Major Polls
To understand the significance of Rasmussen presidential poll results, it is essential to compare them with other major polls conducted by reputable organizations. These comparisons can reveal potential biases, inconsistencies, and overall trends in public opinion.
- Gallup: Gallup is a long-standing polling organization known for its comprehensive surveys on a variety of topics, including presidential elections. Comparing Rasmussen poll results with Gallup data can help identify any discrepancies in voter sentiment or candidate support. For instance, in the 2020 presidential election, Gallup consistently showed a wider lead for Joe Biden over Donald Trump compared to Rasmussen polls. This difference could be attributed to variations in methodology, sample size, or the specific demographics targeted by each poll.
- Pew Research Center: The Pew Research Center conducts extensive surveys on public opinion and social trends, including presidential elections. Comparing Rasmussen poll results with Pew data can provide insights into how voter preferences vary across different demographic groups, such as age, race, and education level. For example, in the 2016 presidential election, Pew polls showed a wider margin of support for Hillary Clinton among younger voters compared to Rasmussen polls. This suggests potential differences in how these organizations sample and weight their data.
- ABC News/Washington Post: ABC News and the Washington Post collaborate on a series of polls that gauge public opinion on a variety of issues, including presidential elections. Comparing Rasmussen poll results with ABC News/Washington Post data can highlight any differences in candidate support or voter sentiment over time. For instance, in the 2018 midterm elections, Rasmussen polls consistently showed a higher level of Republican support compared to ABC News/Washington Post polls. This disparity could be attributed to variations in the timing of the polls, the sampling methods used, or the specific questions asked.
Identifying Trends and Patterns in Rasmussen Presidential Poll Data
Analyzing Rasmussen presidential poll data over time can reveal important trends and patterns in voter sentiment and candidate support. This analysis can shed light on how public opinion is evolving, what factors are influencing voter preferences, and how these dynamics might impact the outcome of the election.
- Changes in Voter Sentiment: Examining the changes in voter sentiment over time can reveal how public opinion is shifting towards specific candidates or issues. For example, analyzing Rasmussen presidential poll data from the 2016 election shows a gradual increase in support for Donald Trump among Republican voters as the campaign progressed. This trend could be attributed to factors such as Trump’s campaign messaging, the media coverage of the election, or the overall political climate at the time.
- Differences in Support Across Demographic Groups: Analyzing Rasmussen poll data can also highlight differences in candidate support across various demographic groups. For instance, in the 2020 presidential election, Rasmussen polls consistently showed a higher level of support for Donald Trump among white voters without a college degree compared to other demographic groups. This finding suggests that candidate support can be influenced by factors such as education level, race, and income.
Analyzing the Potential Impact of Rasmussen Presidential Poll Results
Rasmussen presidential poll results can have a significant impact on the political landscape, influencing media coverage, campaign strategies, and public opinion. Understanding these potential impacts is crucial for understanding the role of polling in elections.
- Influence on Media Coverage: Rasmussen poll results often receive significant media attention, especially during the final months of an election campaign. This media coverage can influence public perception of the race, highlighting potential trends or shifts in voter sentiment. For instance, if a Rasmussen poll shows a significant increase in support for a particular candidate, this could lead to increased media coverage of that candidate and their campaign.
- Campaign Strategies: Campaign strategists closely monitor polling data, including Rasmussen polls, to inform their decisions on messaging, resource allocation, and campaign tactics. If a Rasmussen poll indicates a particular weakness or strength for a candidate, this information could be used to adjust campaign strategies and target specific voter groups. For example, if a Rasmussen poll shows that a candidate is struggling with a particular issue, the campaign might focus on addressing that issue in their messaging and outreach efforts.
- Public Opinion: Rasmussen presidential poll results can also influence public opinion, especially when they are widely publicized and interpreted by media outlets and political commentators. If a Rasmussen poll shows a candidate with a significant lead, this could lead to a “bandwagon effect,” where voters are more likely to support the candidate who appears to be winning. Conversely, if a Rasmussen poll shows a candidate trailing, this could discourage potential supporters and create a sense of inevitability for the other candidate.
The Rasmussen presidential poll, a snapshot of public opinion, often reflects the current political climate. One of the key factors influencing public sentiment is the President’s communication style, which is often on full display during his trump press conferences.
These events, a blend of theatrics and policy pronouncements, have become a focal point for public analysis and discussion, ultimately impacting the Rasmussen presidential poll’s findings.
The Rasmussen Presidential Poll, often a barometer of public sentiment, is keenly watched by political analysts. Its latest findings suggest a tightening race, with the candidates’ performances at the recent Fox presidential debate likely playing a significant role in the shifting dynamics.
Whether this translates into a sustained trend in the polls remains to be seen, but the Rasmussen data offers a valuable glimpse into the evolving political landscape.
