Understanding Meniscus Tears
The meniscus is a C-shaped piece of cartilage that acts as a shock absorber in the knee joint. It helps to distribute weight evenly and protect the joint from wear and tear. It is located between the thighbone (femur) and the shinbone (tibia).
Anatomy of the Meniscus, Meniscus tear recovery
The meniscus is made of tough, rubbery cartilage. It has two parts: the medial meniscus and the lateral meniscus. The medial meniscus is located on the inside of the knee, while the lateral meniscus is on the outside. Both menisci are attached to the ligaments that surround the knee joint.
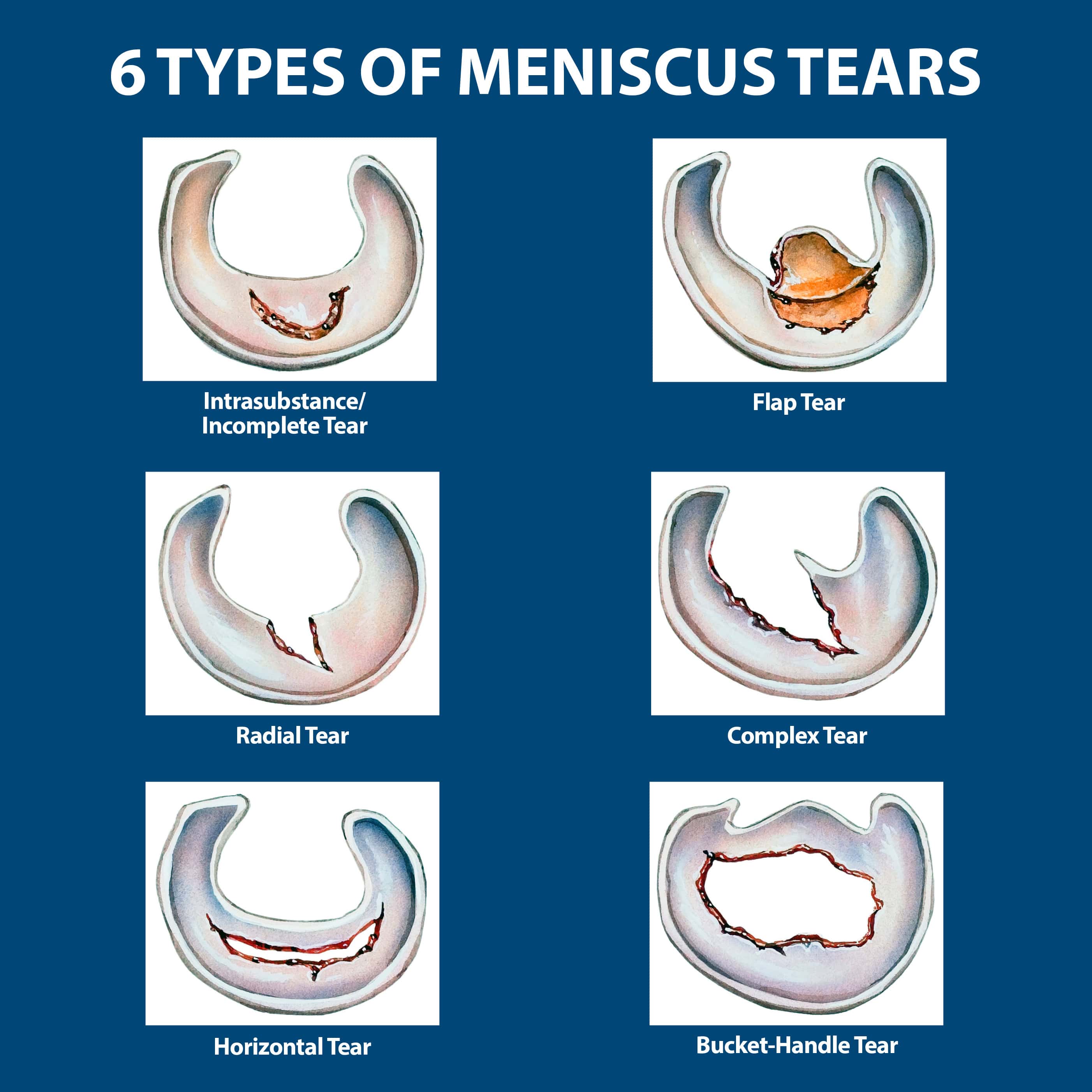
Types of Meniscus Tears
There are different types of meniscus tears, which are categorized based on the location and severity of the tear.
- Horizontal Tear: This type of tear occurs across the width of the meniscus.
- Vertical Tear: This type of tear runs up and down the meniscus.
- Radial Tear: This type of tear is a combination of horizontal and vertical tears.
- Bucket-Handle Tear: This is a serious type of tear where a large piece of the meniscus is torn and displaced.
- Degenerative Tear: This type of tear is caused by wear and tear on the meniscus over time.
Causes of Meniscus Tears
Meniscus tears can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Sudden twisting or pivoting movements: This is a common cause of meniscus tears, especially in athletes.
- Direct impact to the knee: A direct blow to the knee can also cause a meniscus tear.
- Degeneration: As people age, the meniscus can degenerate and become more prone to tearing.
Symptoms of a Meniscus Tear
The symptoms of a meniscus tear can vary depending on the severity of the tear. Common symptoms include:
- Pain: Pain is a common symptom of a meniscus tear, and it may be worse when you twist or bend your knee.
- Swelling: Swelling is also a common symptom, and it may occur immediately after the injury or develop gradually over time.
- Stiffness: Stiffness in the knee joint can make it difficult to bend or straighten the knee.
- Locking: In some cases, the knee may lock in place, making it difficult to move.
- Clicking or popping: You may hear a clicking or popping sound in your knee when you move it.
- Instability: You may feel like your knee is giving way or unstable.
Treatment Options for Meniscus Tears: Meniscus Tear Recovery
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/meniscusfinal-01-5c8fba21c9e77c00010e96f5.png)
A meniscus tear can be a painful and debilitating injury, but the good news is that there are various treatment options available. The best approach will depend on the severity of the tear, your age, activity level, and overall health.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
Non-surgical treatment is often the first line of defense for meniscus tears, especially for minor tears or those in individuals with low activity levels. This approach focuses on reducing pain and inflammation and restoring joint function.
RICE Therapy
RICE therapy stands for Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. It is a common initial treatment for many injuries, including meniscus tears.
- Rest: Avoid activities that aggravate the knee joint, allowing the tear to heal.
- Ice: Apply ice packs to the affected area for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day, to reduce swelling and inflammation.
- Compression: Use a compression bandage to help reduce swelling and provide support to the knee.
- Elevation: Keep the leg elevated above the heart to further minimize swelling.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in meniscus tear recovery. A physical therapist can teach you exercises to strengthen the muscles around your knee, improve range of motion, and enhance stability. They may also use modalities like ultrasound or electrical stimulation to reduce pain and inflammation.
Pain Medication
Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain and inflammation. In some cases, your doctor may prescribe stronger pain medications or anti-inflammatory drugs.
Surgical Treatment Options
Surgery may be necessary for more severe meniscus tears, particularly those that cause significant pain, instability, or locking of the knee. The most common surgical procedure for meniscus tears is arthroscopy.
Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that allows surgeons to visualize and repair the torn meniscus using small incisions and a specialized instrument called an arthroscope. The procedure is typically performed under general anesthesia.
Arthroscopic Repair
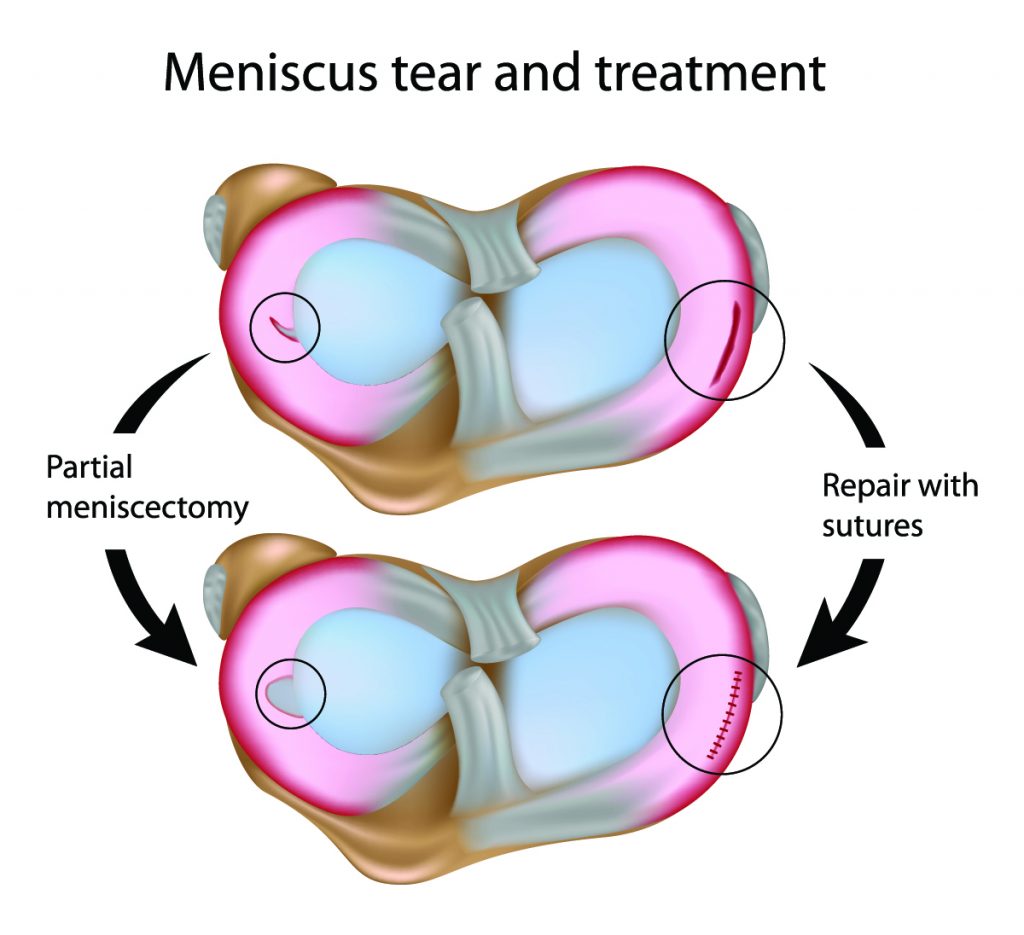
In some cases, the torn meniscus can be repaired by stitching it back together. This is most successful for tears that are located in the outer portion of the meniscus, which has a better blood supply.
Arthroscopic Partial Meniscectomy
If the tear is too severe or located in an area with poor blood supply, the surgeon may remove the damaged portion of the meniscus. This is called a partial meniscectomy.
Comparison of Treatment Options
The choice between non-surgical and surgical treatment options depends on several factors, including the severity of the tear, your age, activity level, and overall health.
| Treatment Option | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Non-surgical Treatment | – Less invasive and less risky – No surgery required – May be effective for minor tears |
– May not be effective for severe tears – May take longer to recover – May not fully restore joint function |
| Surgical Treatment | – Can repair or remove the damaged meniscus – Can provide faster pain relief and improved function – May be necessary for severe tears |
– More invasive and risky – Requires surgery and anesthesia – May have a longer recovery period – May have complications like infection or stiffness |
Recovery Process and Rehabilitation
Recovering from a meniscus tear can take time and effort, and the process varies depending on the severity of the tear and the chosen treatment method. This section Artikels the typical recovery timeline for meniscus tear surgery, including post-operative care and restrictions. It also provides a comprehensive rehabilitation program that includes exercises for strengthening, flexibility, and range of motion, along with tips for managing pain and swelling during the recovery process.
Post-Operative Care and Restrictions
Following meniscus tear surgery, a period of rest and rehabilitation is crucial for proper healing. Post-operative care typically includes:
- Rest and Immobilization: The affected leg may be immobilized with a brace or crutches for a few weeks to prevent further injury and promote healing. The duration of immobilization depends on the type and severity of the tear and the surgical approach used.
- Pain Management: Medications, such as over-the-counter pain relievers or prescription pain medications, may be prescribed to manage pain and inflammation. Ice packs can also be applied to the affected area to reduce swelling.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy is an integral part of the recovery process. A physical therapist will guide you through a tailored exercise program to regain strength, flexibility, and range of motion in the affected leg.
- Weight-Bearing Restrictions: Depending on the surgery and the healing process, weight-bearing restrictions may be imposed to protect the repaired meniscus. These restrictions are typically gradually lifted as the knee heals.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Regular follow-up appointments with your surgeon are essential to monitor the healing progress and address any concerns.
Rehabilitation Program
A comprehensive rehabilitation program aims to restore the knee’s full function and reduce the risk of future injuries. The program typically progresses through different stages, each focusing on specific goals:
Early Stage (Weeks 1-4)
This stage emphasizes reducing pain and inflammation and restoring range of motion. Exercises may include:
- Ankle Pumps: These exercises help improve blood circulation and prevent swelling. While lying down with your leg extended, point your toes up and down.
- Quadriceps Sets: These exercises strengthen the quadriceps muscle, which helps stabilize the knee. While lying down with your leg extended, tighten your thigh muscle and hold for a few seconds, then relax.
- Hamstring Sets: These exercises strengthen the hamstring muscles, which also help stabilize the knee. While lying down with your leg extended, bend your knee and pull your heel towards your buttocks, then relax.
- Straight Leg Raises: These exercises help improve knee extension and strengthen the quadriceps muscle. While lying down with your leg extended, lift your leg a few inches off the bed and hold for a few seconds, then lower it slowly.
- Passive Range of Motion Exercises: These exercises help maintain joint flexibility. Gently move your knee through its full range of motion, without applying force or resistance.
Intermediate Stage (Weeks 4-8)
This stage focuses on increasing strength and endurance. Exercises may include:
- Isometric Exercises: These exercises involve contracting muscles without moving the joint. For example, you can press your knee against a wall or hold a weight with your leg extended.
- Resistance Band Exercises: Resistance bands can be used to provide resistance for exercises like knee extensions, knee flexions, and leg abductions.
- Partial Squats: These exercises help strengthen the quadriceps and hamstrings. Start by standing with your feet shoulder-width apart and slowly lower yourself until your thighs are parallel to the floor. Keep your back straight and your core engaged.
- Calf Raises: These exercises strengthen the calf muscles, which help stabilize the ankle and foot. Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and raise up onto your toes, then slowly lower back down.
- Cycling: Cycling can help improve range of motion and cardiovascular fitness. Start with short sessions and gradually increase the duration and intensity as your knee heals.
Advanced Stage (Weeks 8-12+)
This stage focuses on returning to functional activities and improving proprioception, which is the body’s ability to sense its position in space. Exercises may include:
- Plyometrics: These exercises involve jumping and hopping, which help improve power and explosiveness. Examples include box jumps, jump squats, and single-leg hops.
- Sport-Specific Exercises: These exercises mimic the movements required for your chosen sport or activity. For example, if you play basketball, you may practice drills like dribbling, shooting, and jumping.
- Balance Exercises: These exercises help improve stability and coordination. Examples include standing on one leg, walking on a balance beam, and performing exercises on a wobble board.
- Proprioceptive Exercises: These exercises help improve the body’s ability to sense its position in space. Examples include standing on a foam pad or performing exercises with your eyes closed.
Managing Pain and Swelling
Pain and swelling are common after meniscus tear surgery. To manage these symptoms, you can:
- Rest: Avoid activities that put stress on your knee. Rest is crucial for healing and reducing inflammation.
- Ice: Apply ice packs to the affected area for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day. Ice helps reduce swelling and pain.
- Compression: Wrap the affected area with a compression bandage to help reduce swelling and support the knee.
- Elevation: Keep your leg elevated above your heart when sitting or lying down. This helps reduce swelling by promoting drainage.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Medications like ibuprofen or naproxen can help reduce pain and inflammation.
Meniscus tear recovery – Recovering from a meniscus tear can be a long and challenging journey, filled with physical therapy and adjustments to your daily life. It’s important to remember that you’re not alone in this process, and there are resources available to help you through it.
For example, understanding a similar injury, like a gibbs injury , can offer insight into the healing process and the importance of proper care. With patience and dedication, you can regain your strength and mobility, returning to the activities you love.
Recovering from a meniscus tear can be a tough journey, filled with physical challenges and a longing to get back to the activities you love. Just like the Minnesota Vikings have shown resilience over the years, you too can find strength and determination to overcome this obstacle.
With dedication and the right support, you’ll be back on your feet and ready to tackle life’s challenges, just like the Vikings face their opponents on the field.
